BASIC STRATEGY GUIDE: STEP 2
Activity One (Steps 1-12):
Segment customers, both by size and by need, to identify targets for the Company.
Step 2: Segment all the business’ customers by size
What:
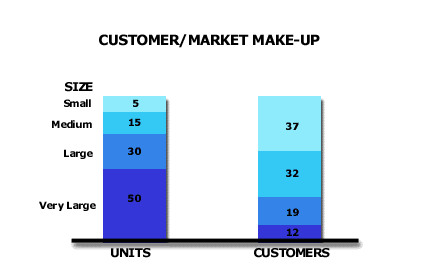
Assign every customer in the market, both those you have as well as those you do not have, and its total purchases from all the industry suppliers into segments defined by the customer’s size of purchases. Use each customer’s dollar volume of total purchases, rather than units of purchases, if customers tend to purchase multiple products from suppliers. Start with the following rough rules that divide customers into four initial segments. Do the segmentation by size of total purchases The segments of number of customers is simply a byproduct.
-
Very Large Customers – the top industry customers, who buy the first 50% of total industry purchase volume. These customers may approximate 7% of the number of customers.
-
Large Customers – the next largest industry customers, who buy the next 30% of total industry purchase volume. These customers may approximate 13% of the number of customers.
-
Medium Customers – the next largest industry customers, who buy the next 15% of total industry purchase volume. These customers may approximate 25% of the number of customers.
-
Small Customers – the remaining industry customers, who buy the final 5% of total industry purchase volume. These customers may approximate 55% of the number of customers.
Customer Size: Industry Examples »
These customer purchase size cutoff points are just starting points. Adjust the size segments to fit the market’s customer make-up. If there is a conflict in using the rules of thumb, this adjustment should set segments by the percentage of industry purchases before the percentage of industry customers.
Determine the stability of the customer size segments by evaluating the percentage of customers in any size segment who change their size segments over some period of time, such as the last three years.
Why:
In every business, segmentation of customers by size is a key first step in developing a strategy. Competition will be greatest for the largest customers. These Very Large and Large customers will tend to buy with similar criteria because large suppliers offer them similar programs. Competition is less intense for the Medium and Small customers in the market place. The Company must separate these size segments from one another in order to understand their different buying patterns and needs. Most of the industry’s competitors will need to serve all of these customer size segments in order to prosper in the market.
What to Watch For:
-
As markets evolve, purchase price and volume allocation to suppliers are likely to be determined by a decision maker above the location taking delivery of the product.
-
When selling to Intermediary customers, the 80/20 Rule often holds. The 80/20 Rule states that the largest 20% of customers account for about 80% of total industry sales. However, with consumers and other Final customers 70/30 is a better beginning estimate for the breakpoint for purchases by the combination of Very Large and Large customers.
-
Check the percentage of customers of each size at the beginning of a period that remain in the same size category throughout the period.
-
Customers of varying sizes often have average growth rates that vary from the average of the whole market.
Action:
Determine the size segments that are most important to the Company. Then identify key competitors for those segments.
More Information on Size of Customer on the Advanced Site>>
For helpful context on this step:
Videos:
Perspectives:
Symptoms and Implications:
